Dictionary of Space Concepts
The Dictionary of Space Concepts (DSC) provides not only the basis for the advanced English language classes of the Multilingualism Programme; it also serves as larger online support platform for all UNIVERSEH students, with the aim of training specific space terminologies across various fields connected to the space sector. The DSC combines core space concepts and with helpful illustrations, all in an open-project format, which is freely available to everyone inside and outside UNIVERSEH. We welcome your contributions, comments, and expertise!
Do you want to take part of developing the Dictionary of Space Concepts? Enrol in the Collaborative Dictionary of Space Concepts.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
E |
|---|
Ephemeris | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: Short definition: An ephemeris is a table or data file that gives the positions of celestial objects at specific times. Detailed Definition: An ephemeris is a detailed table or data file that provides the positions of celestial objects in the sky at specific times. Ephemerides are used in astronomy to predict the future positions of these objects and to understand their orbits and movements. They can be calculated for any point in time and are usually given for a series of times at regular intervals, such as every day or every hour. Initially ephemerides were written, then printed, nowadays, they are digital. Ephemerides of the Solar System play a crucial role in navigating spacecraft. Etymology: ephemeris (Latin) - diary; ephemeris (Greek) - diary, journal Sample Sentence(s): "I consulted an ephemeris to find out when the next solar eclipse would occur." "The astronomer used an ephemeris to predict when the comet would be visible in the sky." "Ephemerides are widely used in astrology." Translations: French: Éphéméride German: Ephemeriden Polish: Efemeryd Swedish: Efemerid Links to videos/articles: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ephemeris https://www.astro.com/swisseph/swepha_e.htm https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons/ | ||
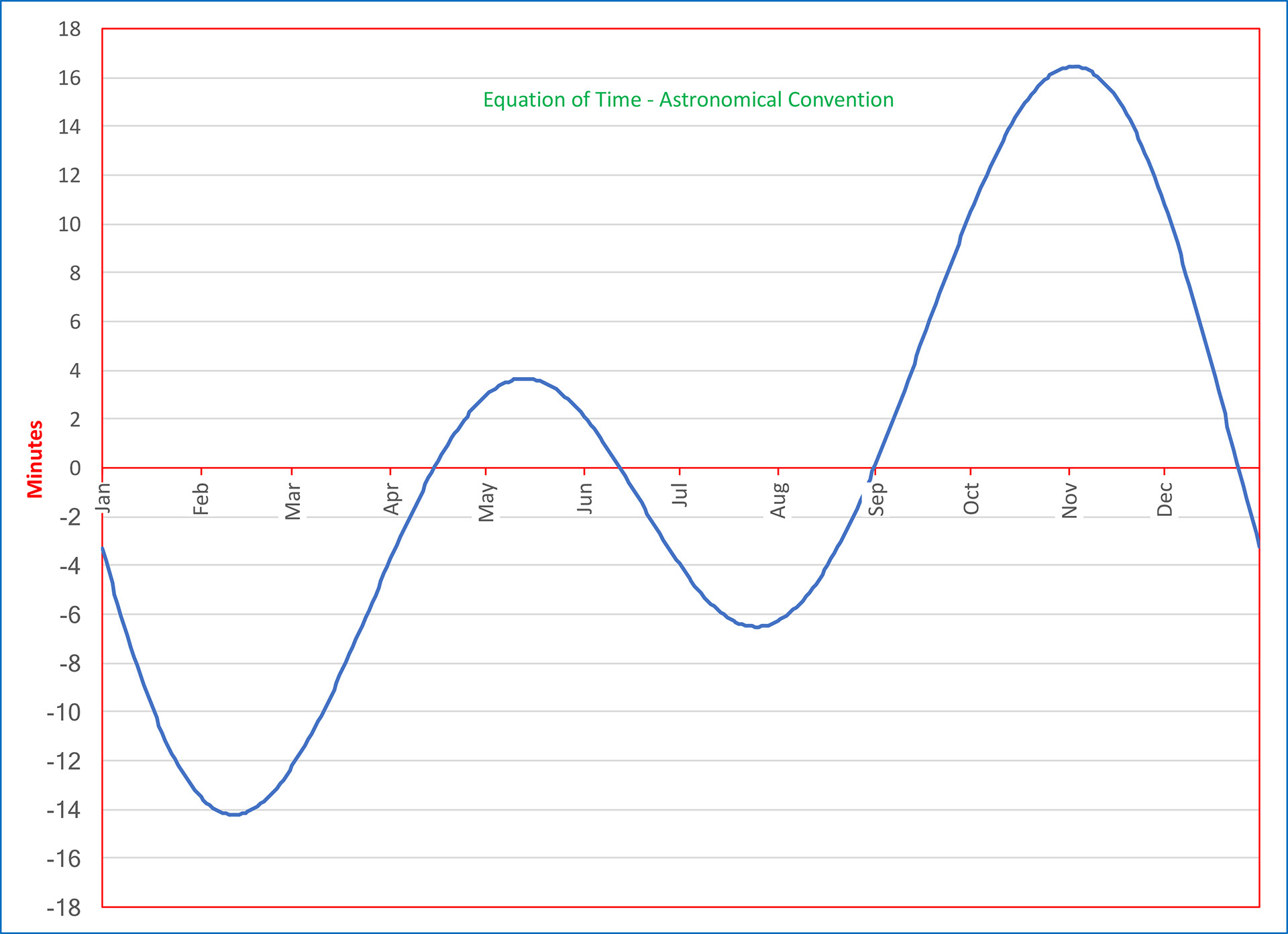
Equation of time | ||
|---|---|---|
Source: https://pro2-bar-s3-cdn-cf3.myportfolio.com/cf59f354b34391ef9ddbec41a1409bef/ece2a825-e54c-4ea4-a57c-bc1f3e901591_rw_1920.jpg?h=e8d9d5ab3208bd43c08d7702b9ec2c74 Short Definition: The equation of time is a result of the difference between the daytime on Earth and the position of the sun. Detailed Definition: The equation of time exists because the orbit of the Earth around the sun is elliptical (where the orbit is not centered around the sun) and not circular which results in a difference in speed around the elliptical orbit as a difference in the length of the Earth days. The equation is the following: EOT =GHA- GMHA where EOT is the equation of time, GHA is the Greenwich Hour Angle of the apparent sun and GMHA is the Universal Time-Off. As a result, the 21./22. December is the shortest day of a year, the real local time (WOZ) results in uneven long hours and the middle time (MOZ) results in a sun orbit, which is unsymmetrical to the time. Etymology: Equation - latin aequationem (" an equal distribution, a sharing in common") Time - Proto-Germanic Timon-/timi ("Time, proper time") Sample Sentence(s): " The equation of time is the reason a Analemma( a diagramm which shows the position of the sun from one point at a specific time over a year) can be seen" Translation: French: équationdutemps German: Zeitgleichung Polish: Równanieczasu Swedish: tidsekvation Links to Videos/Articles: https://youtu.be/Mx9AJJSKIL4 https://astro.dur.ac.uk/~ams/users/equation_of_time.html https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hn0js5EzmEc | ||
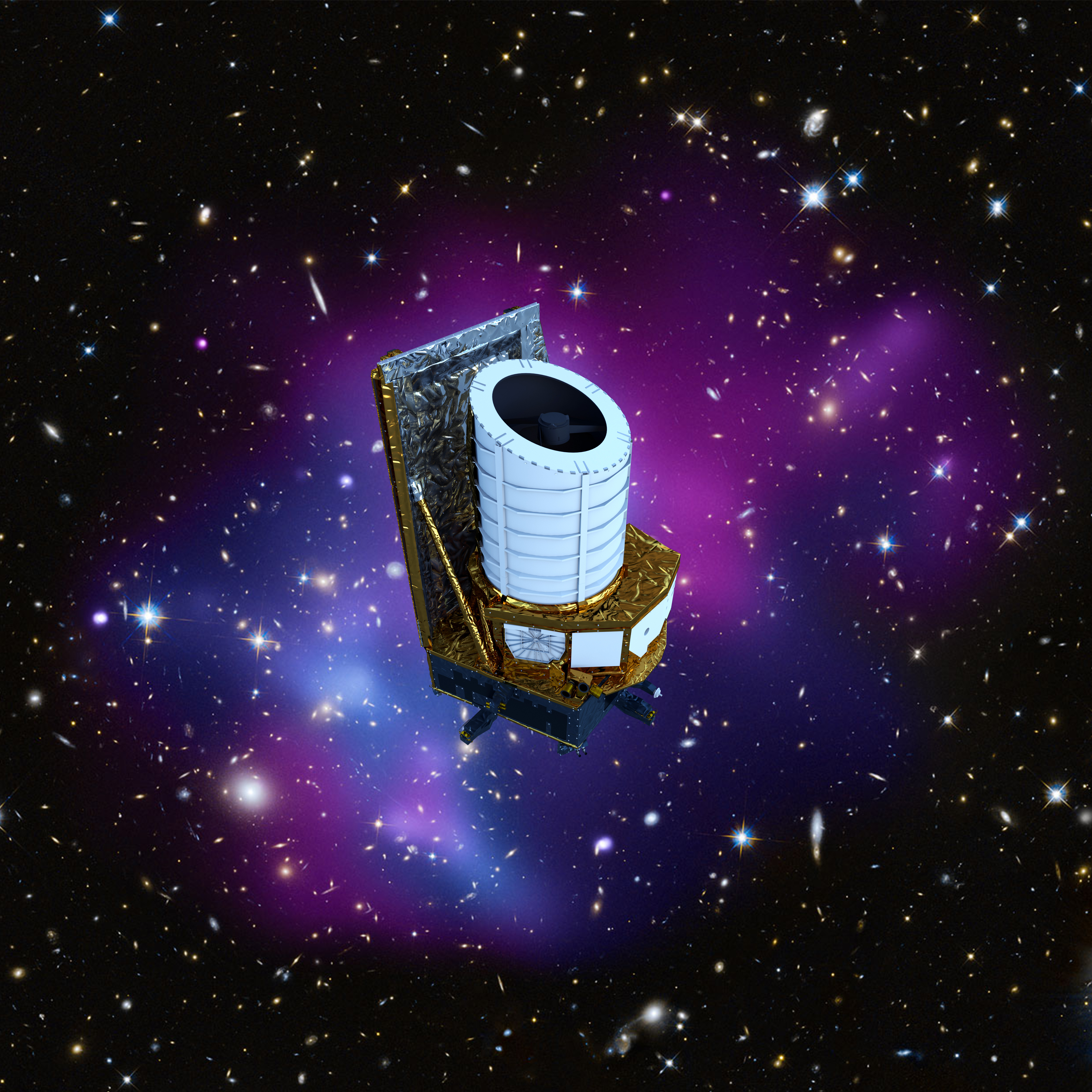
Euclid mission | ||
|---|---|---|
Image source: https://www.esa.int/var/esa/storage/images/esa_multimedia/images/2019/09/euclid_spacecraft/19709645-1-eng-GB/Euclid_spacecraft.jpg Short Definition: The euclid mission is project, being prepared by ESA to investigate dark matter as well as dark energy. At this moment, it is planned to launch the mission in the year 2023 (no specific date is set yet). The planned time the mission will take is set for six years and can be extended, but is limited by the amount of cold gas propulsion. Detailed definition: ESA has started the euclid mission is a project to try to investigate dark matter as well as dark energy. The spacecraft consists of a camera in the visible wavelength and a camera /spectrometer which works in the near-infrared area. It will launch from the Europe'sSpaceport in Kourou, which is located in French Guiana, and will move in an orbit which is halo shaped around the Sun-Earth Lagrange point. Another aspect which will be inspected by the mission is the reason why the expansion of the universe in accelerating and how the evolution of the universe took place, to gain more information about fundamental physics and cosmology. Etymology: Euclid - Greek euclid ("renowned, glorious") mission -Latin missionem ("act of sending a dispatching; a release, a setting at liberty") Sample Sentence: The Euclid mission is expected to bring new knowledge about the history of the universe and dark matter. Translations: French: MissionEuclide German:Euklid-Mission Polish: MisjaEuclid Swedish: UppdragEuclid Links to Articles: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/euclid https://sci.esa.int/web/euclid https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/euclid/main/index.html | ||
EVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
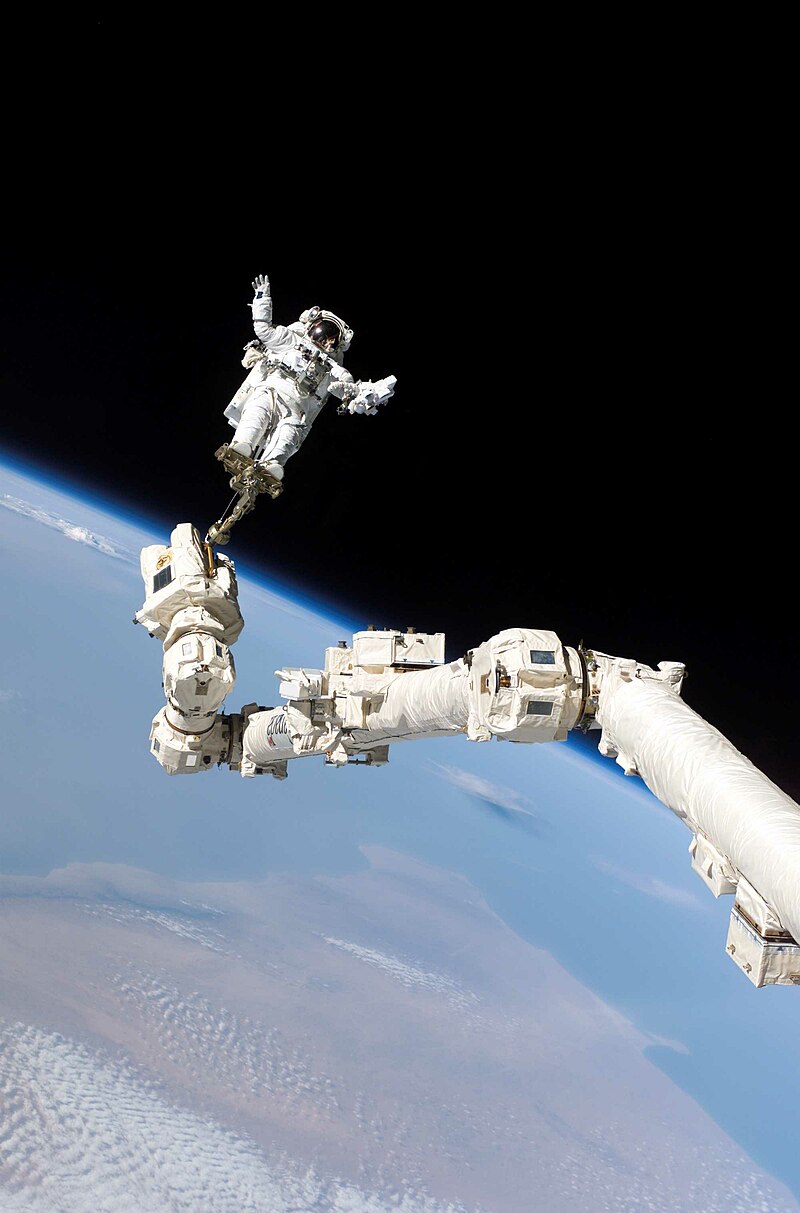 Astronaut Steve Robinson performing an EVA during STS-114 mission. Source: Wikipedia/NASA Short Definition: EVA is an act of performing different activities outside your spaceship while in orbit. This could include repairing, attaching or other experiments. Detailed Definition: Performing an EVA can refer to activities such as spacewalks, where astronauts leave the spacecraft to work in the vacuum of space, as well as other tasks such as inspections or repairs on the exterior of the spacecraft. EVAs are a common part of space exploration and are conducted by astronauts in a variety of different settings, including the International Space Station and during lunar, or in the future, planetary missions. Etymology: EVA stands for Extravehicular Activity Sample Sentence(s): Astronauts on the ISS are preparing to perform an EVA. Yesterday's EVA was completed successfully. Translations: French: Sortie extravéhiculaire German: Außenbordeinsatz Polish: Spacer kosmiczny Swedish: Rymdpromenad Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.nasa.gov/content/extravehicular-activities/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extravehicular_activity | |||
Event Horizon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Source(s): Short Definition: The event horizon of a black hole is a threshold around the black hole where the escape velocity surpasses the speed of light. It is also referred to as a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an observer. Detailed Definition: The term event horizon is used to describe the phenomena of a very strong gravitational pull in the vicinity of a massive and compact object, which is able to prevent even light from escaping. The escape velocity is a threshold value for which the event horizon occurs. It is the velocity needed for an object to overcome the forces acting due to the presence of an enormous mass. If it is greater than the speed of light, it is impossible to witness any event taking place past the event horizon. Etymology: The term was first used by Wolfgang Rindler in the 1950s. Sample Sentence(s): "The event horizon is the ultimate prison wall - one can get in but never get out." - Avi Loeb, chair of astronomy at Harvard University. Translations of Terms/Concepts into Partner Languages French: Horizon des événements German: der Ereignishorizont Polish: Horyzont zdarzeń Swedish: Händelsehorisont Links to Videos/Articles: https://www.space.com/black-holes-event-horizon-explained.html https://astronomy.com/news/2019/04/the-event-horizon-telescope-may-soon-release-first-ever-black-hole-image | |||
Expansion of the universe | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Image/Video/Audio Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expansion_of_the_universe#/media/File:CMB_Timeline300_no_WMAP.jpg Short Definition: The expansion of the universe is a phenomenon, which describes the
inherent property of the universe, where two galaxies that are gravitationally unbound
tend to increase the distance to each other and the rate of expansion is even accelerating.
Far away parts of the observable universe will not be observable in the near
future, because the velocity of expansion is higher than light speed from an
outside perspective. Detailed Definition: The expansion of the universe is a phenomenon, which explains an inherent property of the universe to expand. The fact that the universe seems to expand, was first doubted because of the gravitational force and the fact that releases of energy like the big bang should normally lose power and should slow over time, but the opposite was observed. The elusive culprit was found quite fast. Dark matter is to be responsible for this phenomenon, but since we know even less about dark matter than about the expansion of the universe, details of how and why it expands are still unknown. This expansion occurs at
every location of the universe and only gravitationally bound galaxies will be
able to observe each other, because unbound galaxies will escape our observable
universe at some point. The expansion can in some way be compared to an elastic
rubber band, where the distances also increase when you stretch it, but not
literally and not on a human scale. It is more that at a scale so far zoomed
out, that the universe looks like a cosmic fluid and at this scale it is apparent
that the density is decreasing over time. There are three viable methods to
measure this expansion. One is based on redshifts, while another on the cosmic
distance ladder. Those measurements gave non-matching results, and so 2018 information
from gravitational waves made it possible to determine the rate of expansion
even more precisely. Etymology: Expansion à from Latin expandere à spread out Universeà from Old French univers à from Latin universumSample Sentence(s): In a thought experiment of an ascending civilization in a faraway galaxy in the far future, they would only be able to observe their neighbouring galaxies and will think that this is all there is to the universe and all this due to an expansion of the universe. The rate of expansion of the universe is thought to be accelerating. French: Expansion de l'universGerman: Ausdehnung des Universums Polish: Ekspansja wszechświata Swedish: Utvidgning av universum Links to Videos/Articles: Expansion of the universe - Wikipedia | |||
UNIVERSEH is an alliance of:
All rights reserved. Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.